Real estate appraisal has basics, the real estate appraisal can’t be performed without, which are:
They include identifying:
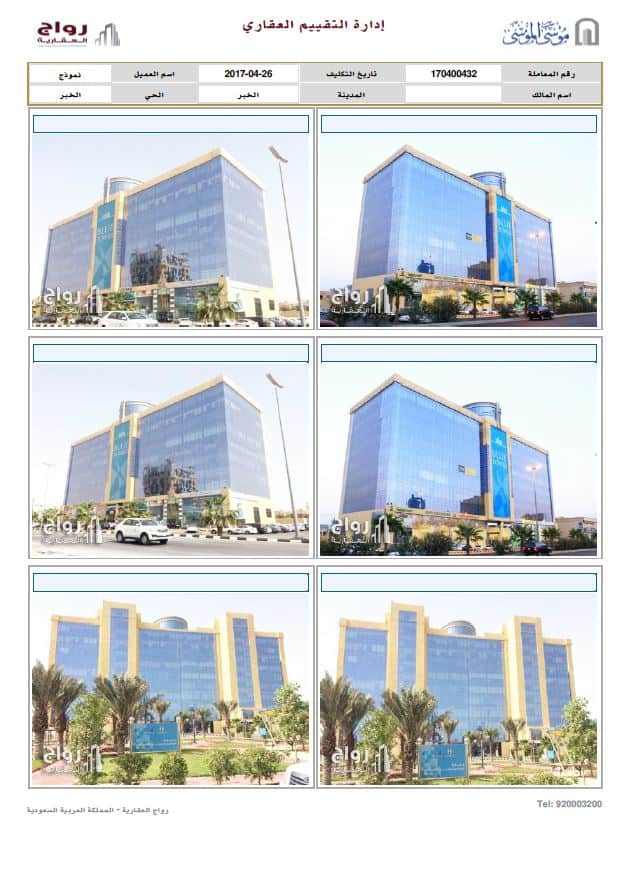
1- Location, and existing buildings.
2- Determination of the type of ownership of the existing property.
3- Determination of the value to be appraised (varies according to the value to be determined).
4- Determination of the purpose of the appraisal (this is done by agreement between the appraisal applicant and the expert).
5- Determination of the date of the evaluation.
6- Determination of any special factors that limit the value of the appraisal: these determinants are to protect the estimator, and inform the report student about the determinants of the evaluation. From the previous information, the most appropriate method for making the appraisal is determined, and in most cases the valid method is only one because it is not possible to collect more information.
Whenever the type of appraisal is determined, the type of information required and appropriate for each method is determined, and the estimator must be familiar with how the information is collected and its sources.
1- General information: (country – province – city – neighboring area).
2- Property information: (location – building).
3- Information on the valuation method: (cost method – previous sale method – income and expenditure capital method).
To determine the market forces pressing for the exploitation of the real estate for the maximum and best use (the highest profitability in using the real estate). This analysis requires taking into account the location, the dimensions of the plot of land, the quality and the plane of the building, all other natural characteristics and the extent to which these properties are compatible with the requirements of the market, meaning whether it serves the best and best use of the market requirements as indicated by market indicators such as supply and demand.
At this stage, the physical properties and services adjacent to the site (not including construction) are compared with their counterparts at nearby sites that have the best and similar use. Based on the foregoing, the land price will be adjusted to reflect the material differences between the valuation site and the comparison sites. From this comparison, and judging by the prices of the neighboring sites, the price of the land is determined (site valuation).
In one of the three known methods:
1 – Cost method.
2 – Method of comparison with previous sales.
3 – Method of calculating the capital value of income.
Usually, the above methods do not produce a single value for the property. The estimator should never take the average value, but the largest weight should be given to the method that has the largest weight compared to other methods that most accurately reflect the property’s value.
This report must contain the determinants within which the report was placed (which is a list of the conditions specified for the validity of the report and specifying the role of the estimator and the general circumstances under which the report was placed). This is to protect the estimator firstly and to clarify the circumstances of the report to the reader secondly. The report also contains a certificate from the evaluator to confirm the steps that he followed to prepare the report for the benefit of the report applicant, the provisions for conformity of the various evaluation reports, and to judge the report in a unified manner.